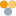RFID systems use two (2) separate antennae; one on the Transponder (RFID Tag) and one (or more) on a reader (interrogator).
RFID systems use radio transmissions via these antennae at prescribed frequencies to send energy to a Transponder (RFID Tag) that may be in reading range.
Each Transponder receives this signal and returns its unique identification code as a greeting. This greeting indicates that the tag is present in its read range.
Once a reader (interrogator) senses an RFID Tag, it can request any additional information from the RFID Tag that may also be encoded on it. This information is then stored and/or processed by the information management system to which the RFID system is attached.
The RFID system can also be used to re-write or append information to the RFID Tag based upon the results of processing.